Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in perianal Crohn's disease at 1.5 and 3.0 T: a feasibility study
Diagnostics (Basel) 11(11)
Imaging biomarkers of inflammation and treatment response across joints and organ systems.

Bioxydyn has delivered multiple studies for pharmaceutical companies using quantitative imaging of inflammation in a wide range of diseases, including functional imaging of joints in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and renal imaging in nephritis.
We use dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) to quantify changes in perfusion and endothelial integrity in the presence of inflammation and during treatment. Bioxydyn has defined many of the standard approaches to the technique's implementation in clinical trials.
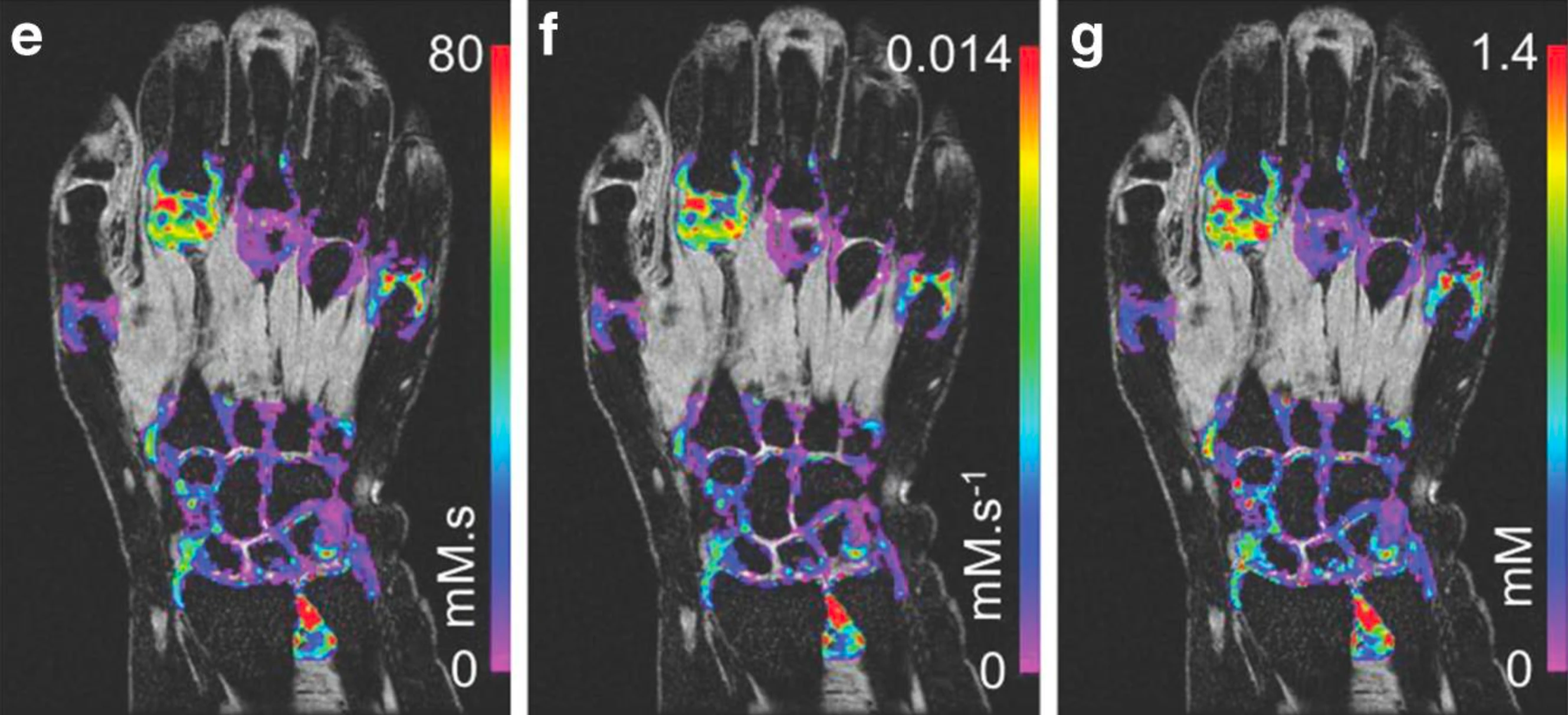
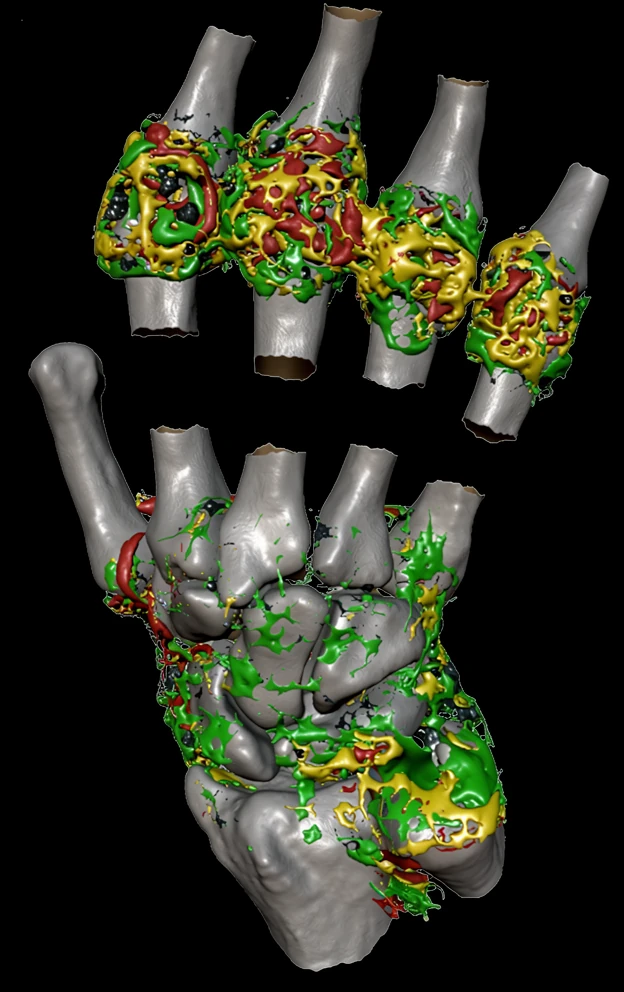
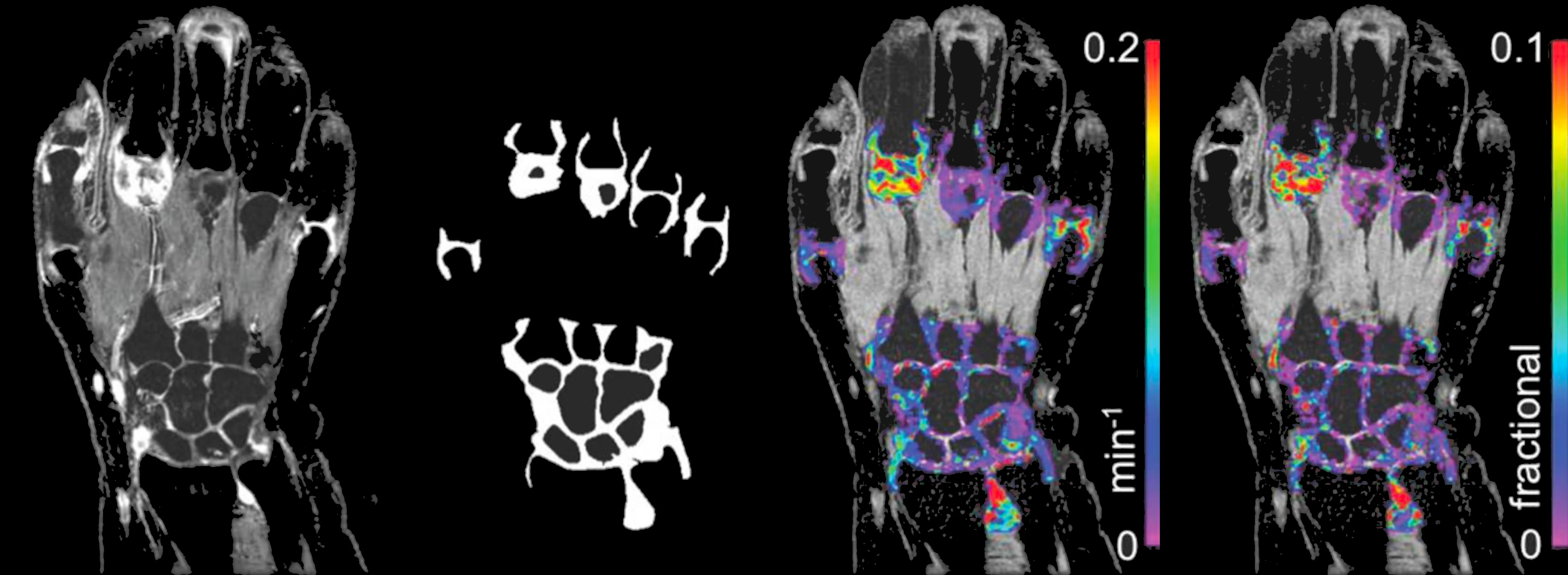
DCE-MRI involves standard clinical gadolinium-based contrast agents. The uptake and washout of the agent are interpreted with physiological modelling methods to provide imaging biomarkers of microvascular function and inflammation.
Bioxydyn uses the Ktrans quantitative biomarker, which can be readily compared between centres. Its relationship to the intensity of inflammation is based on sound, accepted science, is extremely sensitive to drug effects, and often requires only small patient numbers.
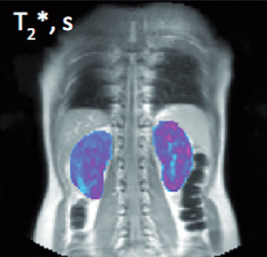
Bioxydyn is experienced in using MRI biomarkers of inflammation and fibrosis in kidney disease, including perfusion from ASL, relaxation time measurements (T1, T2, T2*), volume measurements, and diffusion MRI (ADC, FA). We are also experts in methods to measure hypoxic status (BOLD, oxygen-enhanced MRI) and pH (CEST).
Publications supporting inflammatory disease biomarkers, including mechanistic trials and DCE-MRI validation.

Diagnostics (Basel) 11(11)
Eur Radiol 31(8):5746-5758

Lancet Rheumatol 2(11):e666-e676
Why it matters: Phase 2a mechanistic study linking DCE-MRI biomarkers with therapeutic response.
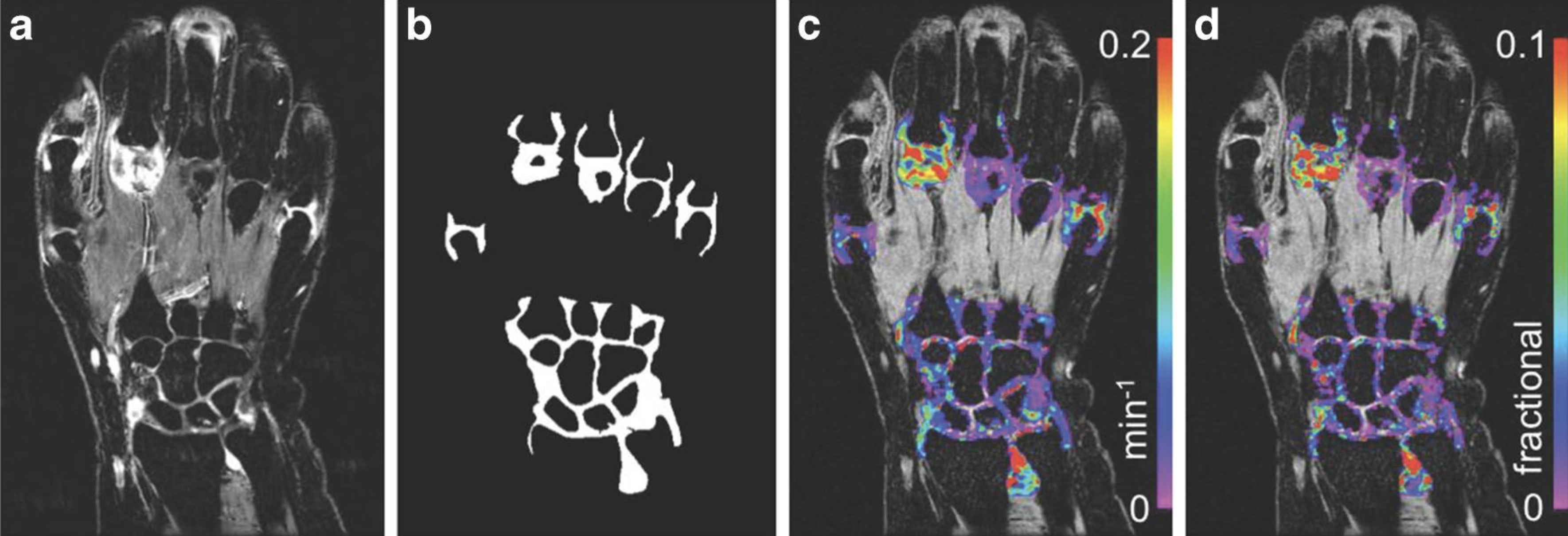
Lancet Rheumatol 2(10):e623-e632
Eur Radiol 27(9):3662-3668